如何使用 Eloquent 處理一對一的資料?
除了傳統關聯式資料的Join外,Laravel的Eloquent還提出了Relation,這兩個看似相同的東西,事實上還是有些差異,其相關的SQL與Blade寫法也不太一樣。
Version
PHP 7.0.0
Laravel 5.2.6
關聯性資料
依然使用最經典的users與posts table,由於本文只討論一對一關係,也就是一個user只有一篇post,其中primary key為users.id,foreign key為posts.user_id。
條件在users
使用Join
Repository
1 | namespace App\Repositories; |
使用join()去描述users與posts的關係。
使用where()去篩選條件,因為users與posts都有id欄位,所以在where()要明確指定哪一個table的id。
SQL
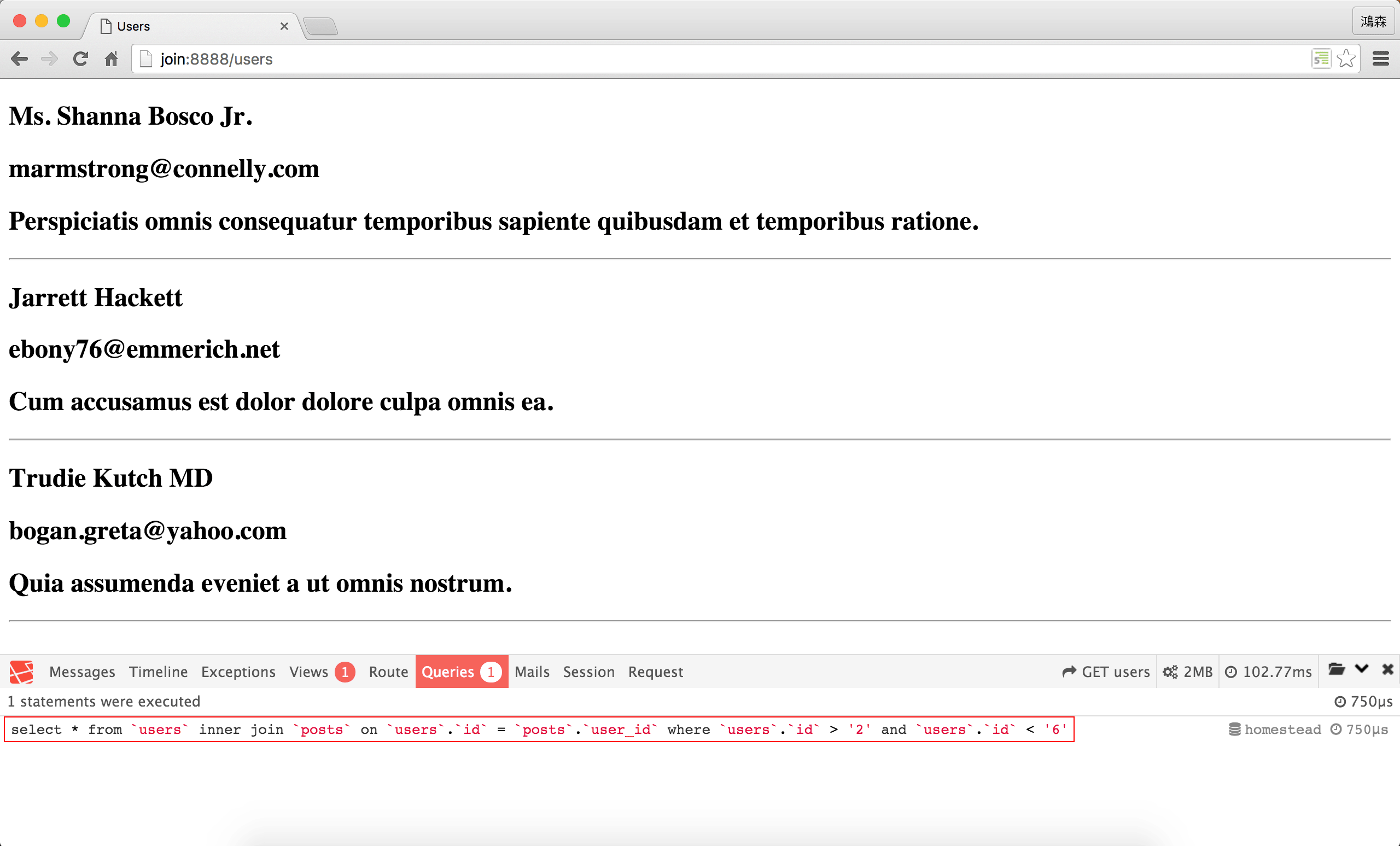
若使用Laravel Debugbar去觀察,可以發現Eloquent產出的是一句SQL,如我們所預期。1 1關於Laravel Debugbar,詳細請參考如何使用Laravel Debugbar?
Blade
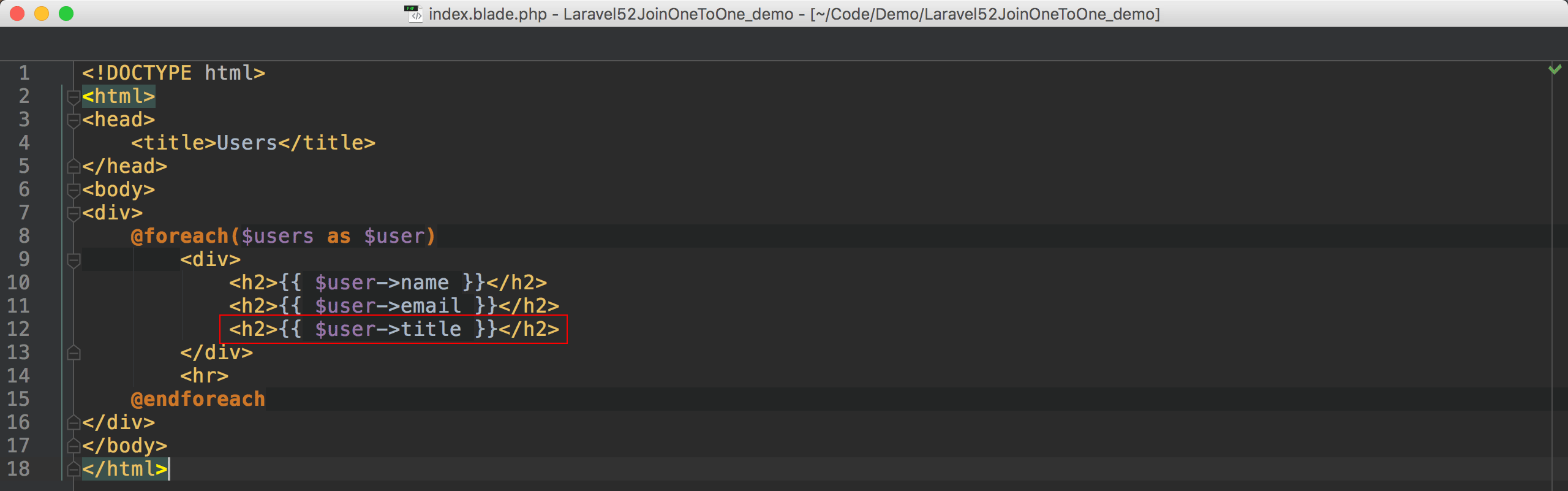
由於Eloquent產出的是1句SQL,回傳的是一個collection,所以title雖然是在posts table,但經過join之後相當於在同一個table,因此在Blade中存取title如同存取users其他欄位一樣。2 2完整程式碼在我的GitHub
使用Relation
Model
1 | namespace App; |
31行1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/**
* users與posts為一對一關係
*
* @return HasOne
*/
public function post() : HasOne
{
return $this->hasOne(Post::class);
}
新增post(),描述users與posts的一對一關係,hasOne()的第一個參數傳入為一對一關係的class字串。3 3若foreign key的命名依照pararent tabel單數名稱 + id的命名方式,Laravel將可自動抓到foreign key與primary key的對應關係,不用特別指定。
Repository
1 | namespace App\Repositories; |
不指定任何relation。
使用where()去篩選條件,雖然users與posts都有id欄位,但where()只作用在users,所以不用明確指定哪一個table的id。
SQL
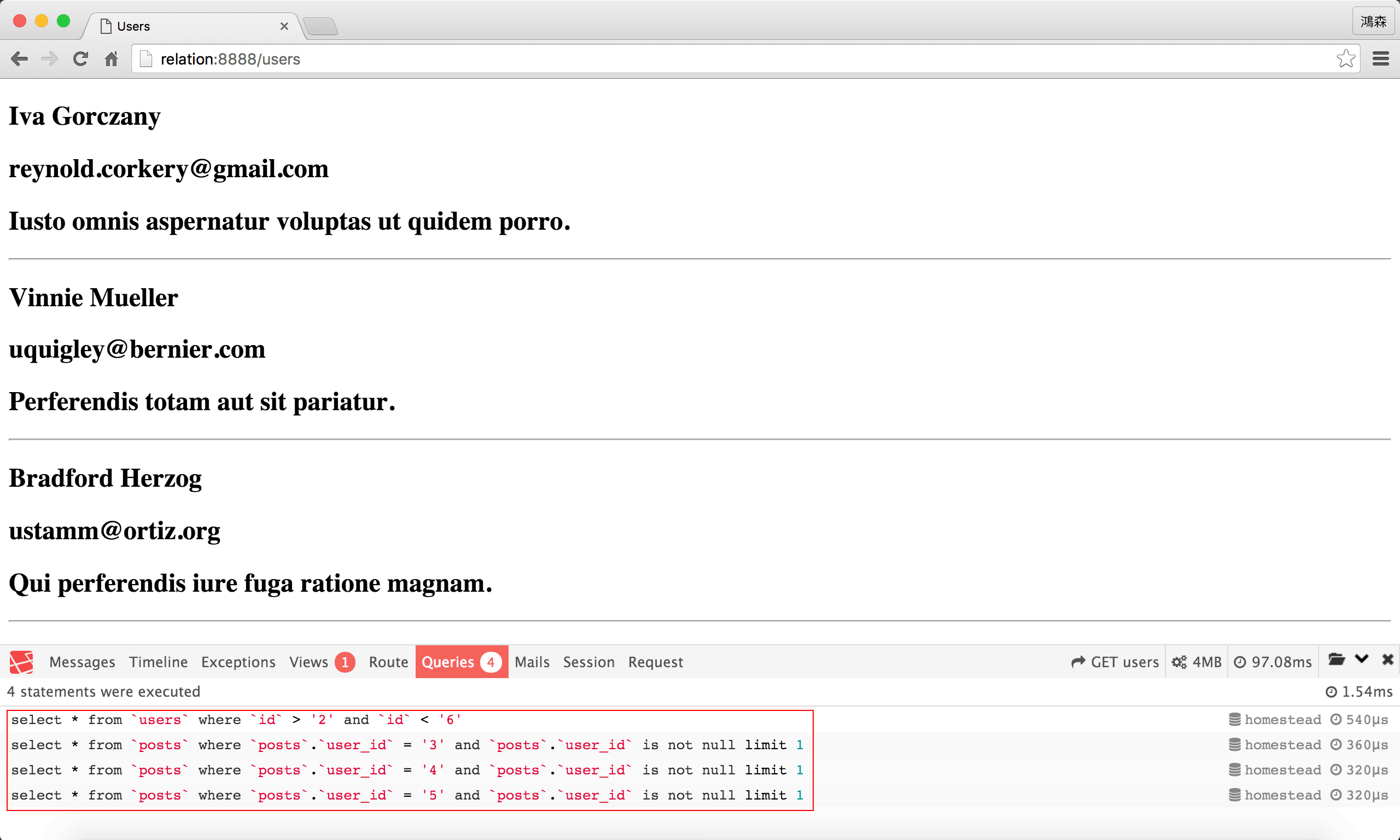
雖然結果完全一樣,但產生的SQL卻不一樣。
使用relation後,可以發現Eloquent產出了4句SQL,而where()全落在第1句SQL,這也是為什麼儘管id欄位重複,在where()卻不用特別指定table名稱。
若結果posts有n筆資料,則會產生 (n + 1) 句SQL。
Repository
1 | namespace App\Repositories; |
使用with()指定要使用哪一個relation。
使用where()去篩選條件,雖然users與posts都有id欄位,但where()只作用在users,所以不用明確指定哪一個table的id。
SQL
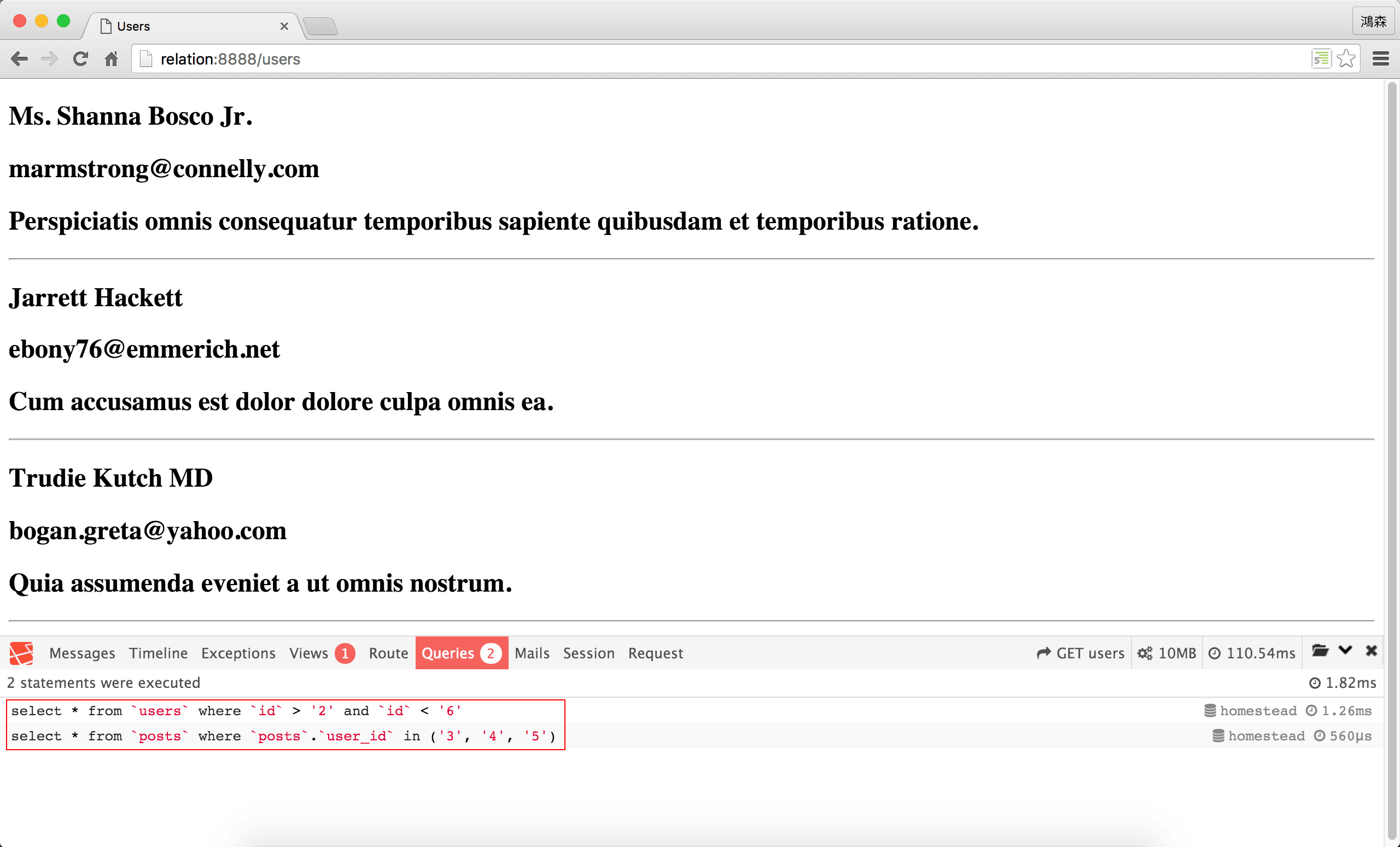
雖然結果完全一樣,但產生的SQL卻不一樣。
使用with()後,可以發現Eloquent只產出了2句SQL,而where()全落在第1句SQL,這也是為什麼儘管id欄位重複,在where()卻不用特別指定table名稱。
Blade
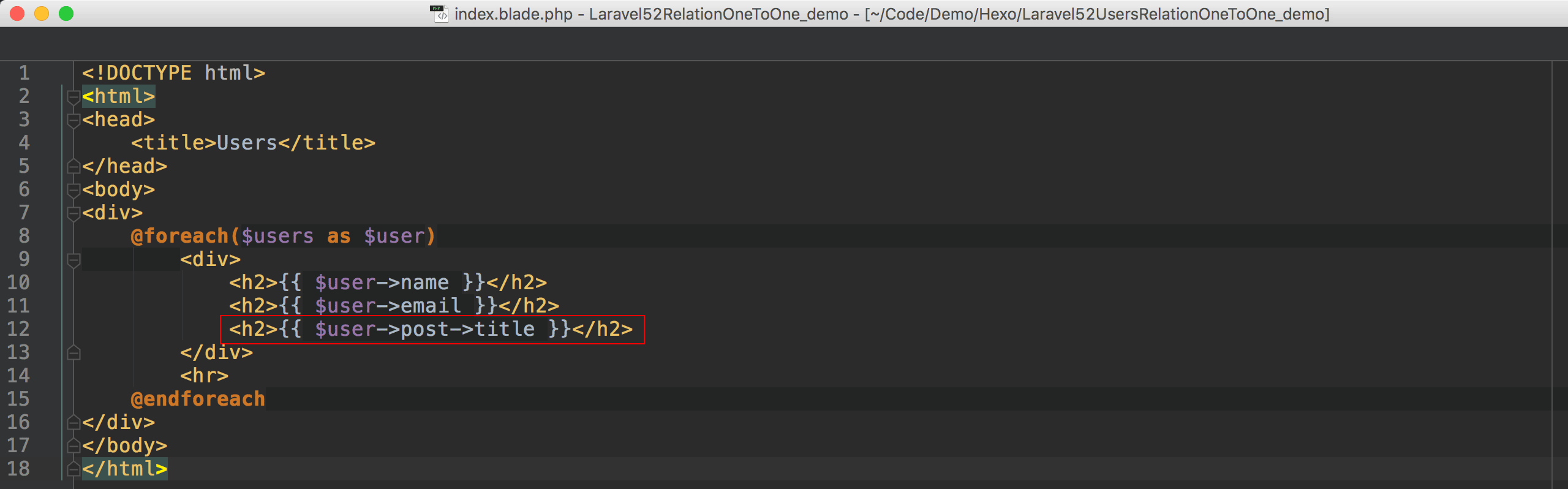
由於Eloquent產出的是2句SQL,回傳的是兩個collection,因此Blade在存取title時,必須透過post()這個relation去存取。4 4完整程式碼在我的GitHub
條件在posts
前面的範例,where()條件都落在users,已經發現Join與Relation的寫法之差異,但實務上不可能條件都落在users,也會落在posts,這樣該怎麼寫呢?
使用Join
Repository
1 | namespace App\Repositories; |
15行1
->where('posts.id', '<', 6)
將where()條件改到posts上。
SQL
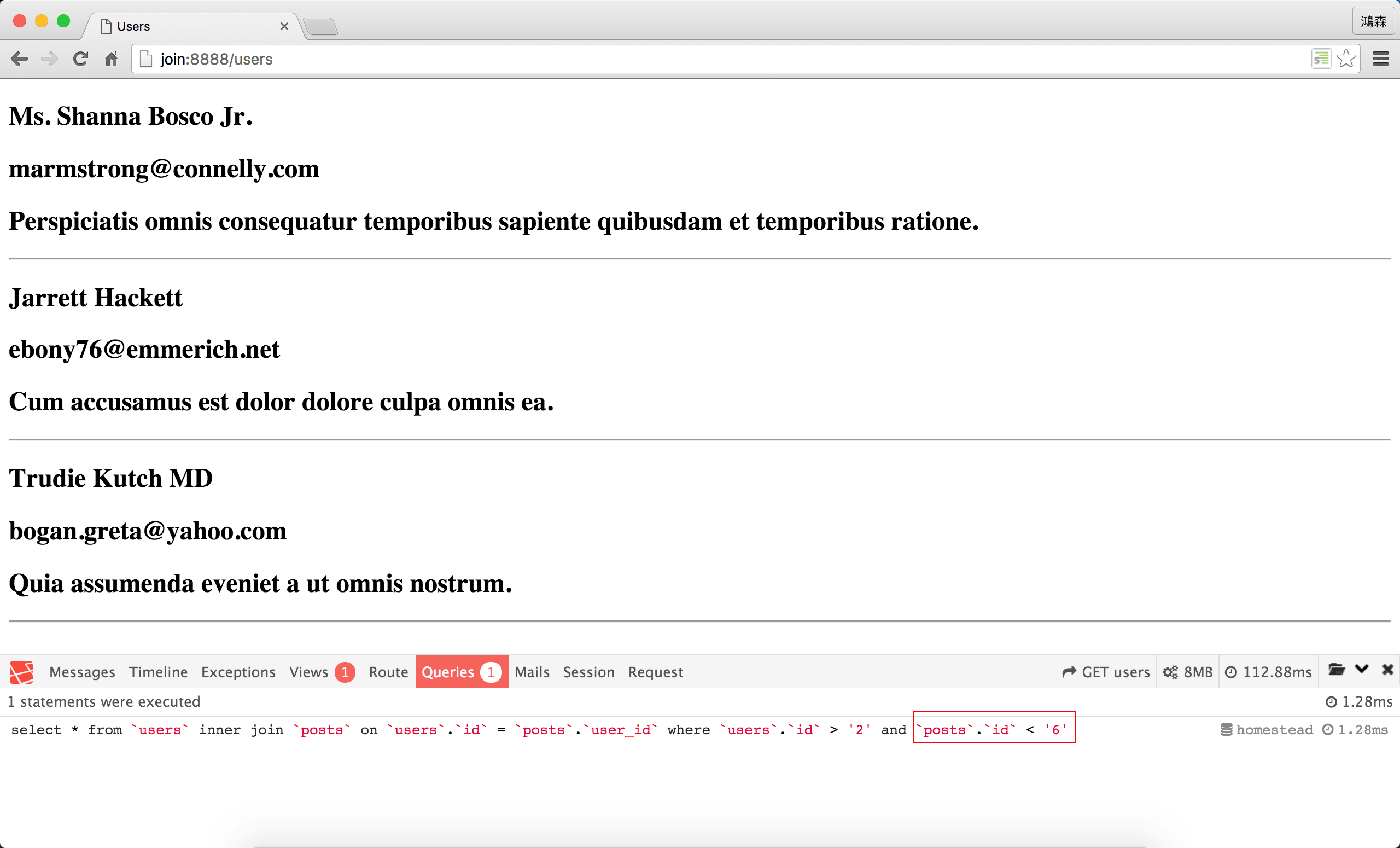
執行結果一樣,但SQL的條件已經從users.id改成posts.id,符合我們預期。
Blade

Blade則完全一樣,不必修改。5 5完整程式碼在我的GitHub
使用Relation
Repository
1 | namespace App\Repositories; |
因為users與posts都有id欄位,直覺只要在id前面加上table名稱即可。
但一執行就會出現錯誤。
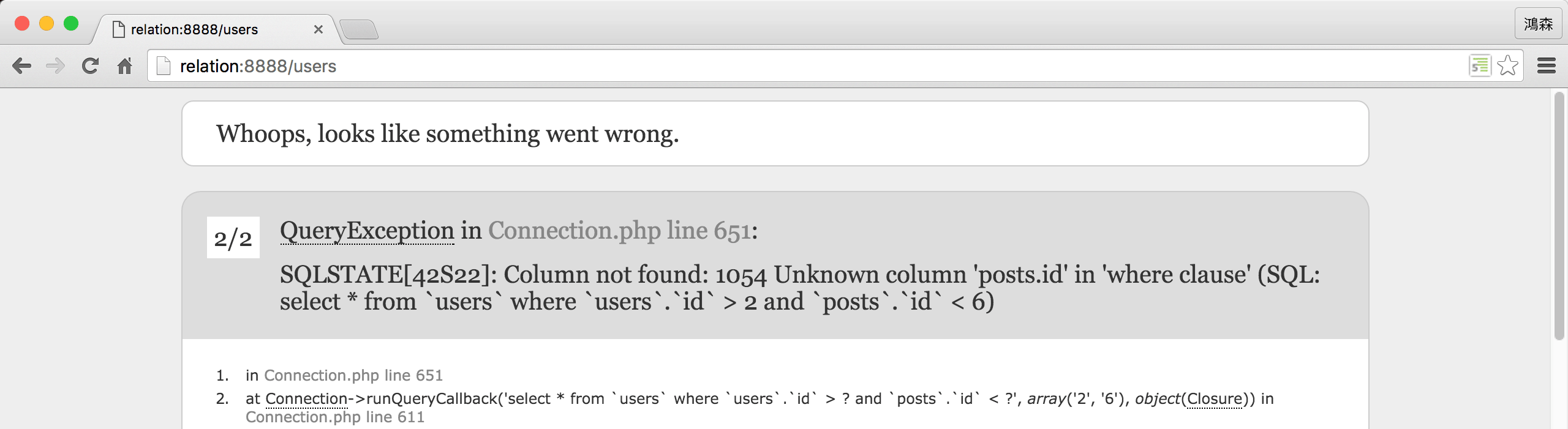
還記得之前在relation下where()條件時,所有的條件都會落在users嗎? 因為都落在users,所以自然找不到posts.id這個欄位。
1 | namespace App\Repositories; |
若要將where()下在posts,必須改用這種寫法,在closure內下where()條件。
SQL
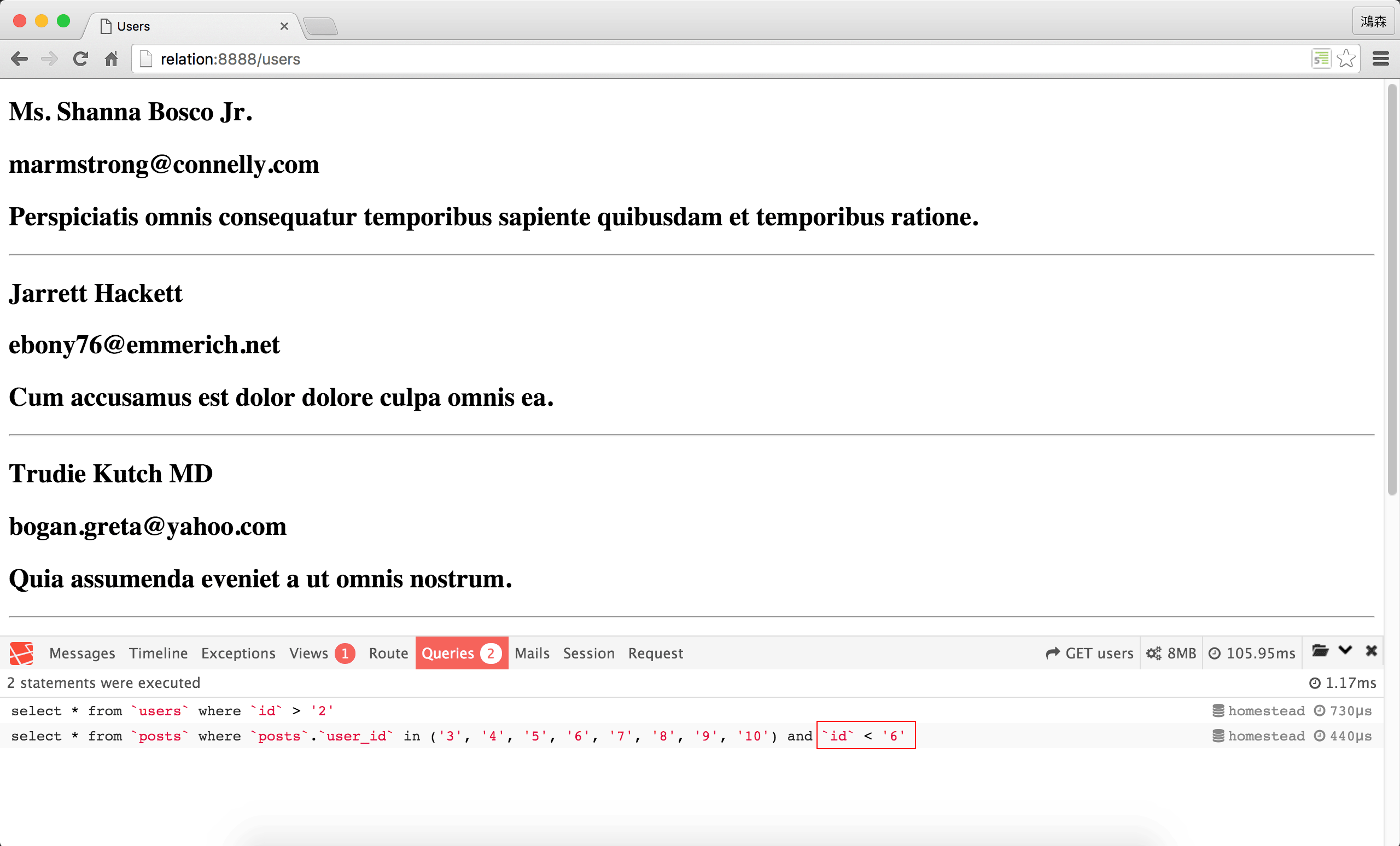
where()條件雖然加到posts上了,但結果是錯的。
Blade
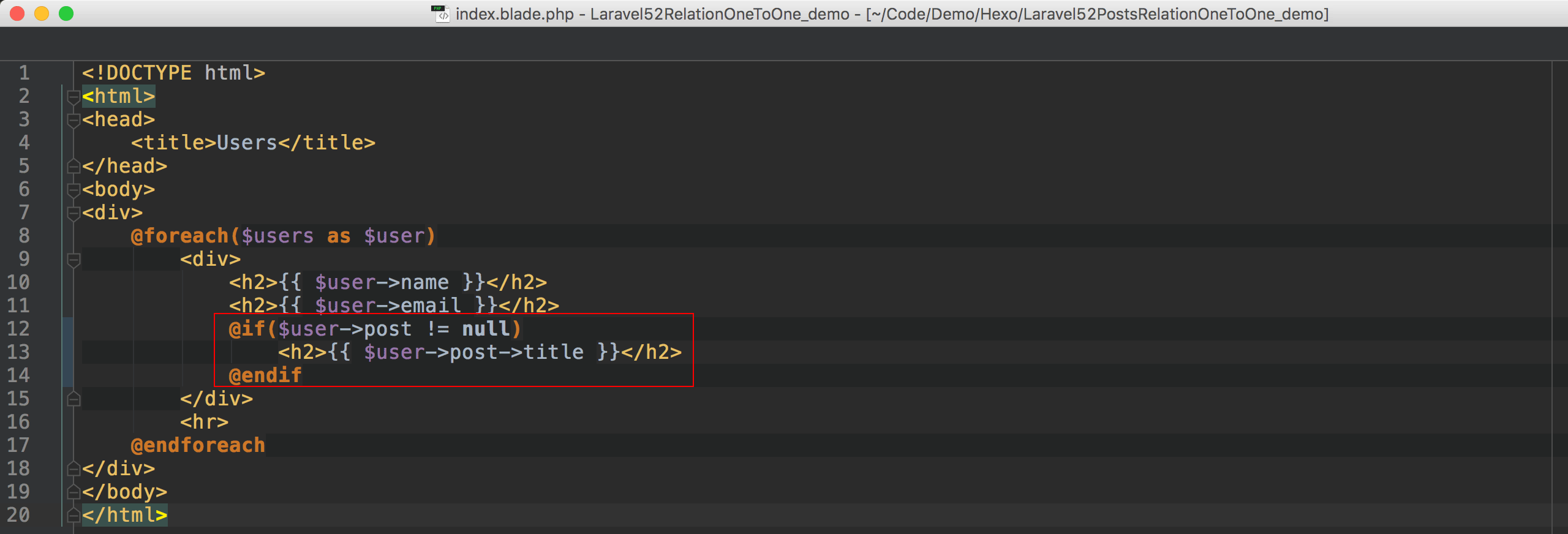
加了posts.id < 6的條件之後,其實7, 8, 9, 10都不成立,所以不一定有post物件,需要特別判斷是否為null。6 6完整程式碼在我的GitHub
Conclusion
- 使用relation寫法,看似只是將原本join的條件式改寫到model內,但事實上SQL與結果完全不一樣,還順便影響了Blade的寫法。
- Relation寫法並沒有辦法取代join,有些join用relation還是寫不出來,relation只能讓我們的工具箱多一種處理關聯式資料的工具,必須自己依照實務上的需求,決定該使用join還是relation。
Sample Code
完整的範例可以在我的GitHub上找到。
- 條件在
users - 條件在
posts